Venipuncture, the process of drawing blood or administering intravenous therapy, is a critical skill in medical practice. The arm and hand are the most common sites for venipuncture due to their accessibility and the availability of suitable veins. Understanding these sites is essential for healthcare professionals and those in training, as it ensures efficient and effective patient care. We will explore the key venipuncture sites on the arm and hand and provide tips on how to improve your venipuncture skills using practice models from Ultrassist.
Venipuncture Sites in the Arm
The arm is the preferred site for venipuncture due to the accessibility and size of the veins. Here are the most common sites:
- Median Cubital Vein: Located in the antecubital fossa, this vein is the most commonly used site for venipuncture due to its size and ease of access. It's typically less painful and has a lower risk of complications.
- Cephalic Vein: Found along the lateral aspect of the arm, this vein is a good alternative when the median cubital vein is not accessible.
- Basilic Vein: Located on the medial side of the arm, this vein is less commonly used due to its proximity to arteries and nerves but can be a good option in certain situations.

Forearm Venipuncture Sites
While less common than the antecubital fossa, the forearm can also be used for venipuncture:
- Cephalic Vein: Extends down the lateral side of the forearm and is often visible and palpable.
- Basilic Vein: Continues down the medial side of the forearm but requires careful technique to avoid nearby structures.
Venipuncture Sites on the Hand
The hand is another site for venipuncture, especially in patients with difficult arm veins:
- Dorsal Metacarpal Veins: These veins are located on the back of the hand and are often used for IV cannulation.
- Cephalic Vein: Extends into the dorsal hand and can be accessed for venipuncture or IV therapy.
- Basilic Vein: Also extends into the dorsal hand, though it is less commonly used.

Dorsal Hand Venipuncture
The dorsal hand veins are useful for venipuncture in cases where arm veins are not suitable. These veins are often visible and easy to palpate, making them an excellent option for IV access.
Tips for Successful Venipuncture
- Choose the Right Site: Selecting the most suitable vein based on the patient’s anatomy and the purpose of the venipuncture is crucial.
- Proper Technique: Ensuring correct needle insertion angle and depth to avoid complications.
- Practice Regularly: Using IV practice models can significantly enhance your skills.
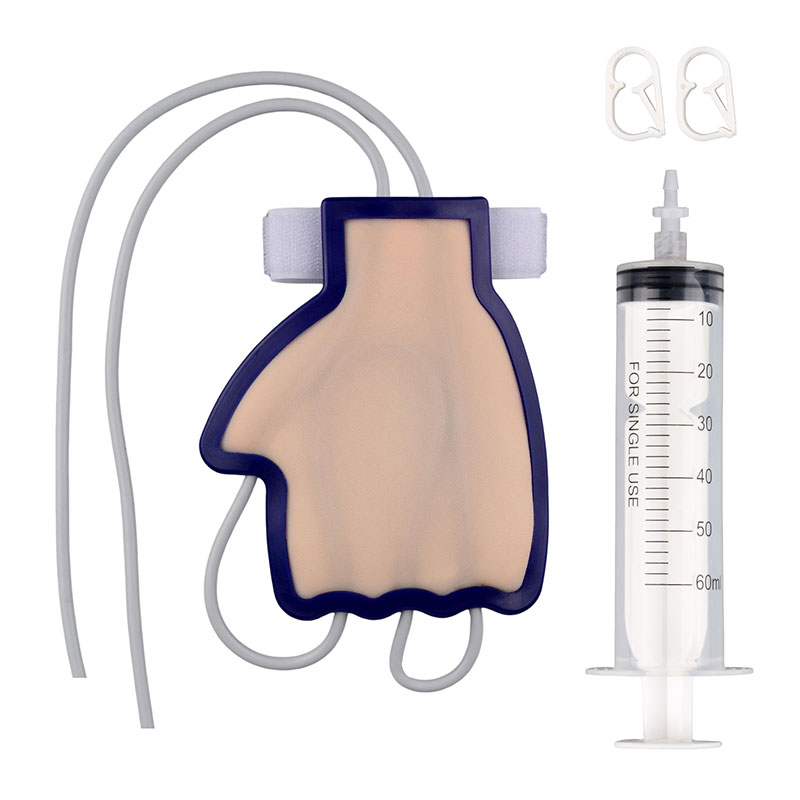
Using IV Practice Models from Ultrassist
At Ultrassist store, we offer high-quality IV practice models that help you master venipuncture techniques. Our models are designed to simulate real-life scenarios, providing a realistic experience for training.
- Realistic Anatomy: Our models accurately replicate the anatomy of the arm and hand, allowing you to practice venipuncture in the most common sites.
- Durability: Built to withstand repeated use, our models are perfect for ongoing training and skill enhancement.
- Versatility: Suitable for both novice and experienced practitioners, our IV practice models cater to all skill levels.
You can improve your technique and confidence by learning how to select venipuncture site and practice venipuncture regularly with realistic IV simulation models from Ultrassist. Visit our website to explore our range of Venipuncture IV and Phlebotomy Practice Kits and elevate your venipuncture skills.





.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)

.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)


.jpeg?w=800&h=800)
.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)





.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)