What Is Neonatal Resuscitation?
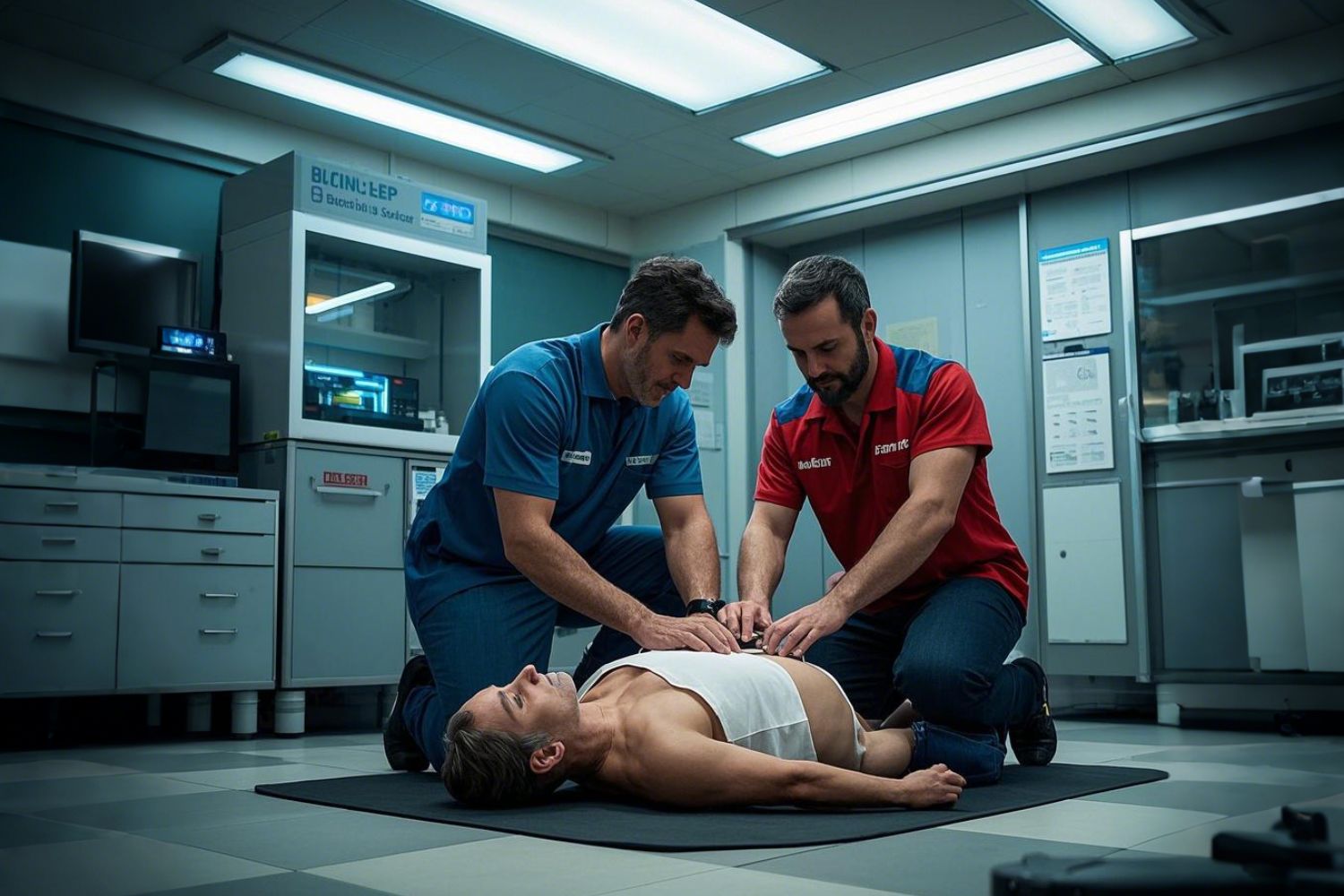
Neonatal resuscitation refers to emergency interventions provided to newborns who fail to breathe adequately at birth. About 10% of newborns need some assistance, and a small number require extensive resuscitation involving ventilation, chest compressions, and medication.
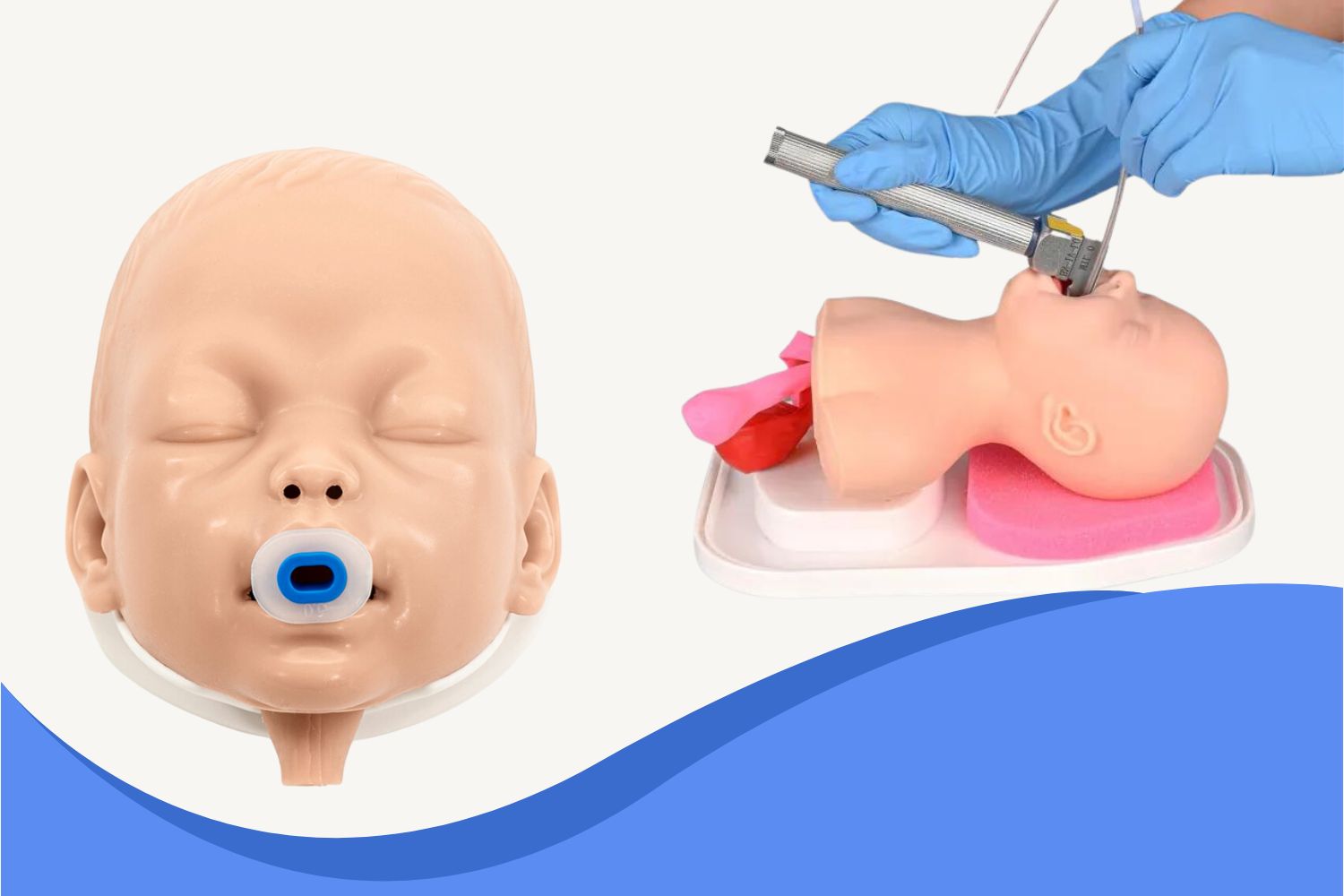
To improve outcomes, simulation-based training with realistic tools such as the Ultrassist Neonatal Intubation Trainer is key in preparing healthcare providers for these high-stakes moments.
➤ What Are the Goals of NRP?
The NRP curriculum is designed to help providers:
-
Recognize signs of neonatal cardiopulmonary distress
-
Initiate effective resuscitation when needed
-
Master airway management (mask ventilation and intubation)
-
Coordinate ventilations and chest compressions
For hands-on training, the Neonatal Intubation Trainer and CPR Training Kit offer realistic practice to reinforce these critical skills.
➤ The Four Components of Neonatal Resuscitation
-
Ventilate the lungs safely
-
Use oxygen judiciously
-
Apply chest compressions effectively
-
Administer medications or fluids when needed
The Ultrassist CPR Training Kit allows learners to practice 3:1 compression-ventilation techniques - a core element of neonatal resuscitation.
➤ What Is the Most Important Step?
Ventilation is the single most critical intervention in neonatal resuscitation. It must be optimized before moving to compressions. Training on realistic manikins like the Neonatal Intubation Trainer builds the confidence to act decisively.
➤ Three Initial Evaluation Questions:
Before beginning any resuscitation efforts, assess:
-
Is the baby full-term?
-
Is there good muscle tone?
-
Is the baby breathing or crying?
These quick questions help determine whether routine care or advanced support is needed.
➤ Compression-Ventilation Ratio
3:1 ratio is recommended. 90 compressions and 30 ventilations per minute. Repeated practice with the Portable CPR Kit helps learners internalize this pace.
➤ Who Should Take NRP?
NRP is essential for:
-
Nurses & nurse-midwives
-
Neonatologists and pediatricians
-
Respiratory therapists
-
Emergency medical professionals
-
Delivery room staff
Simulation tools like those from Ultrassist help multidisciplinary teams build shared competence.
➤ Why NRP Training Matters
The Neonatal Resuscitation Program® not only teaches theory - it emphasizes:
- Realistic simulation
- Effective team communication
- Critical thinking under pressure
This is where tools like the Ultrassist Neonatal Intubation Trainer and CPR Training Kit bridge the gap between learning and doing.
Recommended Training Tools for NRP Skills
| Skill | Recommended Trainer | Product Preview |
|---|---|---|
| Ventilation & Intubation | Pediatric Intubation Trainer |  |
| Ventilation & Intubation | Infant Intubation Trainer |  |
| Chest Compressions | Hands-Only CPR Training Kit |  |
| Chest Compressions | CPR Training Model with Sound Feedback | .jpg?w=1000&h=1000) |
Ready to Practice Your NRP Skills?
Explore all Airway Management Trainers to enhance neonatal care training with lifelike models trusted by educators worldwide.



.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

