When securing an airway becomes a matter of life or death, two procedures often come into play: cricothyrotomy and tracheostomy. Though both provide airway access, they serve different clinical purposes and are performed in very different contexts.
For healthcare professionals, especially those working in emergency medicine or critical care, understanding when and how to perform each procedure is crucial, and so is hands-on training.
What is Cricothyrotomy?
Cricothyrotomy is an emergency procedure used when other airway management methods, such as intubation or supraglottic devices, have failed or are impossible. It involves making an incision through the cricothyroid membrane, just below the Adam's apple, to establish airflow.
Indications:
- Acute upper airway obstruction (e.g., trauma, foreign body, anaphylaxis)
- "Can't intubate, can't oxygenate" (CICO) scenarios
- Facial trauma or massive swelling
Procedure Summary:
- A vertical skin incision is made over the cricothyroid membrane
- A horizontal incision opens the airway
- A tube is inserted to establish airflow
Advantages:
- Fast and life-saving in emergencies
- Can be performed with minimal equipment
Limitations:
- Only suitable for short-term use (hours to a day)
- Higher risk of complications if performed by untrained providers
What is Tracheostomy?
Tracheostomy is a planned surgical procedure typically performed in an operating room or ICU. It creates a direct opening in the trachea, below the level of the cricoid cartilage, for long-term airway support.
Indications:
- Prolonged mechanical ventilation
- Neuromuscular conditions affecting breathing
- Chronic upper airway obstruction
- Post-head or neck surgery
Procedure Summary:
- Horizontal incision in the lower neck
- Dissection to expose the trachea
- Insertion of a tracheostomy tube
Advantages:
- Provides a stable airway for weeks or months
- More comfortable for long-term ventilated patients
Limitations:
- Not appropriate for emergencies
- Requires surgical expertise and sterile environment
Cricothyrotomy vs. Tracheostomy: Quick Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cricothyrotomy | Tracheostomy |
|---|---|---|
| Setting | Emergency | Surgical / ICU |
| Speed | Immediate (<1 min) | Planned (15–30 min) |
| Duration | Temporary | Long-term |
| Location | Cricothyroid membrane | Trachea (below cricoid) |
| Tools Needed | Basic emergency kit | Surgical instruments |
| Performed By | EMS, ER, battlefield medics | ENT surgeons, ICU teams |
When to Choose Which?
- Cricothyrotomy is the last-resort life-saving measure when all other airway options have failed. Think battlefield trauma, crush injuries, or severe burns.
- Tracheostomy is preferred in the ICU or OR when long-term airway management is anticipated, such as in ventilated stroke or ALS patients.
Training is Critical - Practice Before the Crisis
Both procedures carry significant risks if performed incorrectly. For this reason, hands-on simulation training is non-negotiable, especially for emergency responders and prehospital providers.
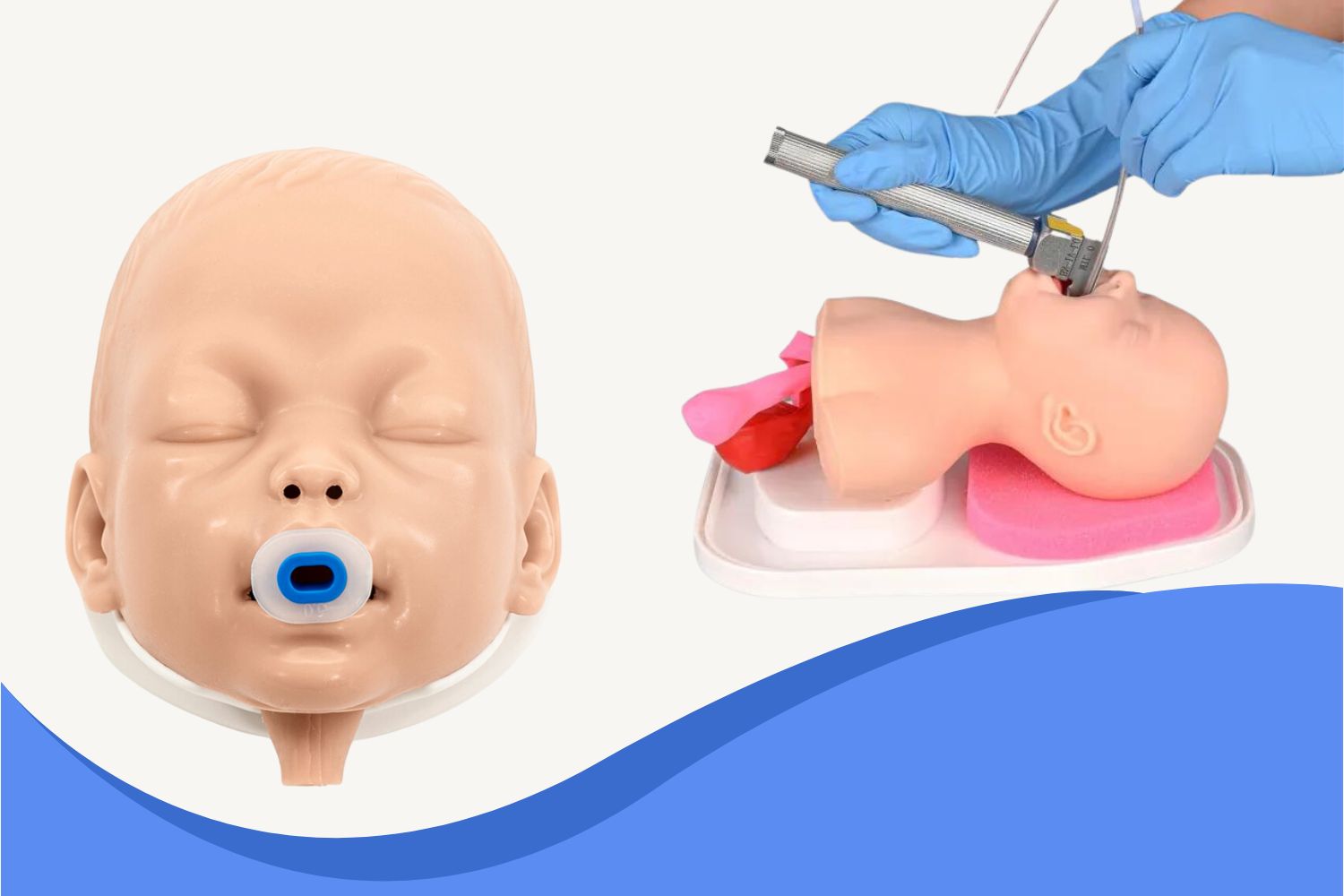
Recommended Cricothyrotomy Trainers from Ultrassist
- Wearable Cricothyrotomy Trainer
A portable, wearable trainer that allows users to practice in real-time emergency settings—ideal for EMS and tactical medics.
Key Features:
- Realistic skin texture
- Anatomical landmarks for blind or visual access
- Designed for field simulation or classroom use
- Cricothyrotomy Task Trainer
A higher-fidelity model suitable for repeat practice and training centers.
Key Features:
- Replaceable membranes and skin for multiple attempts
- High realism for scalpel insertion and tube placement
- Ideal for trauma surgeons, ER residents, and airway instructors



.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

