Precision in Practice: Neonatal Intubation Guidelines
Neonatal intubation is a high-stakes procedure that demands accuracy, preparation, and continuous skill refinement. Adhering to standardized guidelines not only improves success rates but also reduces complications in vulnerable newborns.
Key Guidelines for Neonatal Intubation
1. Patient Assessment & Stabilization
Evaluate respiratory effort, heart rate, and overall condition. Stabilize the newborn before initiating intubation.
2. Team & Equipment Preparation
Ensure clear communication and assign roles. Check all intubation tools, including laryngoscope, suction device, and appropriately sized endotracheal tubes.
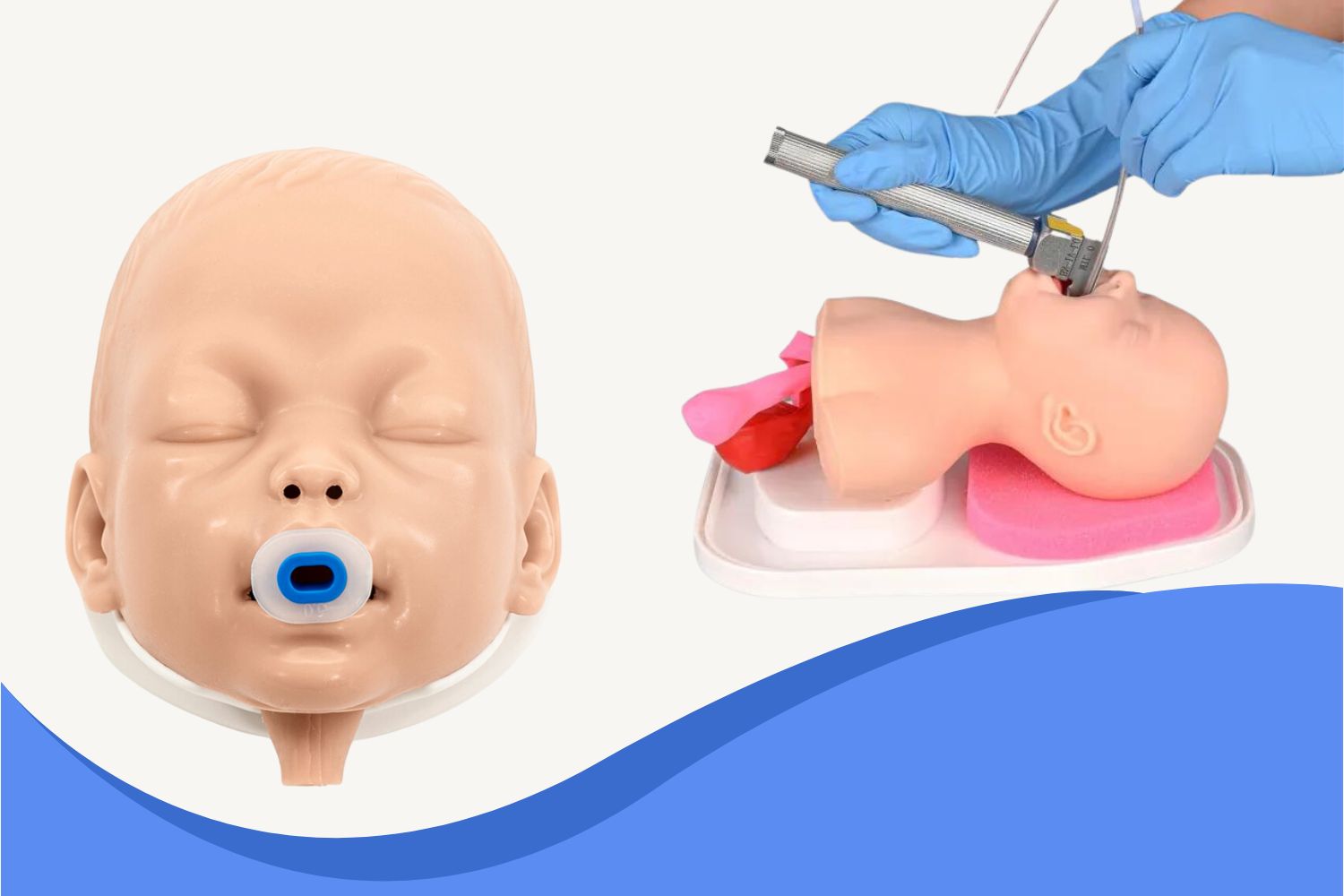
3. Proper Positioning
Use the "sniffing" position to align the airway axes. Our Neonatal Intubation Trainer is designed to help users practice and master correct positioning techniques.
4. Preoxygenation
Deliver oxygen to achieve optimal saturation before laryngoscope insertion.
5. Medication Considerations
Administer sedation and analgesia when necessary, based on the infant's condition and procedure urgency.
6. Suctioning
Clear the airway of fluids or meconium to ensure visibility and ventilation.
7. Tube Size & Selection
Choose tube size based on gestational age or weight. Monitor cuff pressure if using cuffed tubes.
8. Intubation Technique
Insert the tube gently under direct visualization of the vocal cords. Avoid tissue damage or improper placement.
9. Confirmation of Placement
Check for chest rise, bilateral breath sounds, and use capnography to confirm CO₂ detection.
10. Tube Securing
Secure the tube to prevent accidental dislodgement. Document depth at the lips or nose.
11. Post-Intubation Care
Initiate appropriate ventilator settings and continuously monitor vital signs.
12. Record Keeping
Document all procedure details, including tube size, depth, time, medications used, and clinical response.
13. Ongoing Assessment
Reassess regularly to determine continued need and adjust support as needed.
Train with Realism. Perform with Confidence.
To master these critical skills, we recommend training with the:
▶ Ultrassist Neonatal Intubation Trainer
Designed for both orotracheal and nasotracheal intubation practice, this trainer replicates neonatal airway anatomy with lifelike feedback. It’s ideal for simulation labs, NICU teams, and emergency responders.
Want more? Explore our Intubation Manikins for complete support in clinical airway education.



.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

