Neonatal endotracheal intubation is a high-stakes procedure that demands precision, training, and confidence. Because of the unique anatomical challenges presented by newborns, repeated practice using realistic models is essential to ensure successful airway management in emergency or NICU settings.
This guide walks you through the essential neonatal intubation steps, equipment checks, and methods for confirming placement, backed by simulation training with the Ultrassist Neonatal Intubation Trainer.
Pre-Procedure Checklist
Before beginning the intubation process, ensure the following equipment is ready:
- Fully functional laryngoscope with working light (check battery in advance)
- Sterile 3.0 mm endotracheal tube (ETT) for neonates
- Sterilized catheter core (stylet) as backup
- Resuscitation bag (Ambu bag) for ventilation
- Stethoscope for auscultation
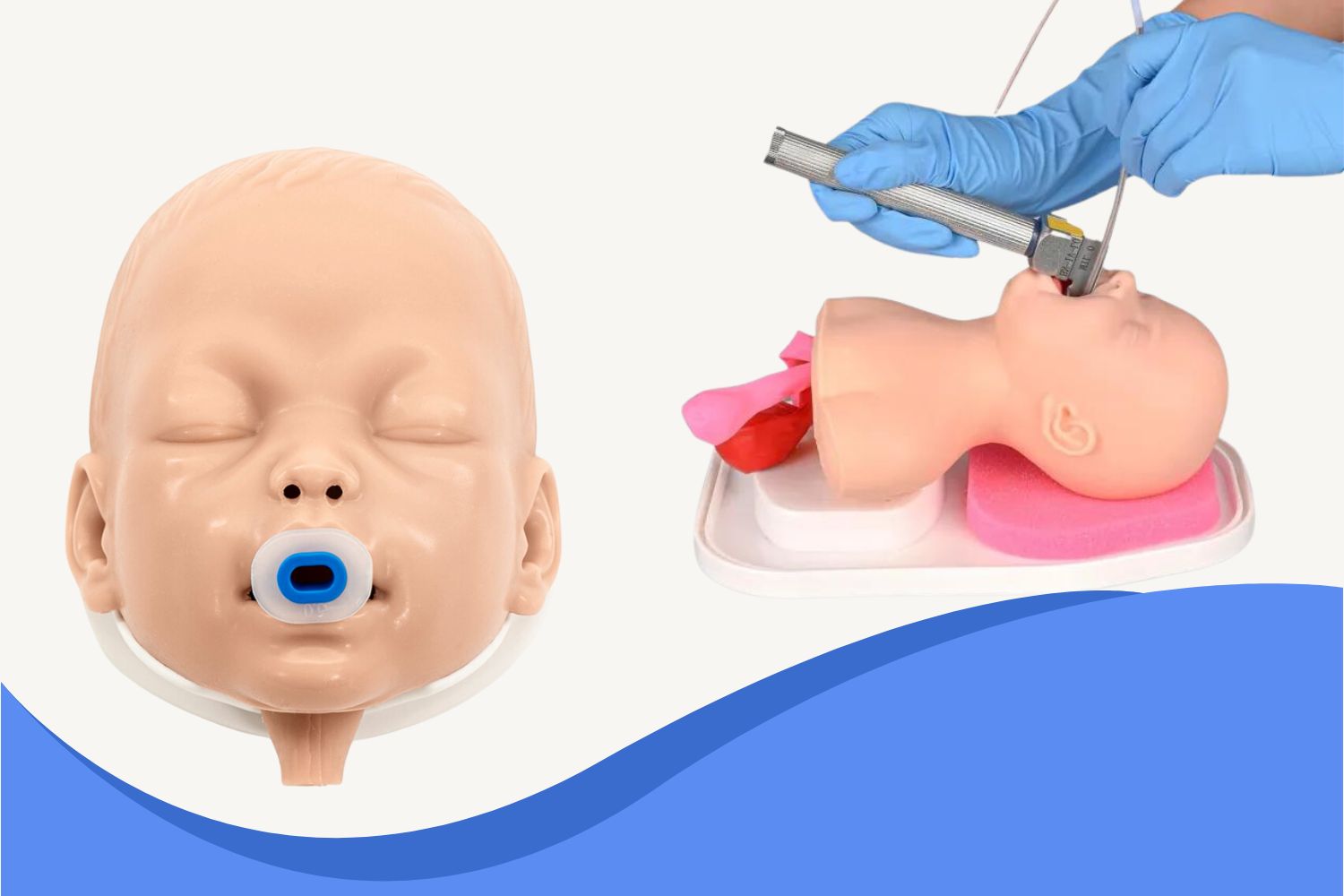
- Intubation trainer (for simulation practice)
🎓 Tip: Practicing with a neonatal airway management trainer enhances muscle memory and reduces real-world error rates.
Step-by-Step Neonatal Intubation Technique
Step 1: Position the Patient
Place the neonate flat on the bed with the operator’s upper abdomen or lower chest at the same level as the infant’s head.
Maintain a "sniffing" or nasoaspiratory position by gently tilting the neck and placing a small 2 cm pad under the shoulders. This improves visualization of the airway.
🛠 Ultrassist Pediatric Intubation Trainer is anatomically designed to simulate this optimal position—no manual adjustment required.
Step 2: Insert the Laryngoscope
- Slide the blade along the right side of the tongue, displacing it to the left.
- Advance to the epiglottic vallecula without applying pressure to the soft tissue.
- Lift the entire blade gently to expose the vocal cords.
- Apply cricoid pressure if needed to enhance visibility.
Step 3: Insert the Endotracheal Tube (ETT)
- Advance the ETT along the right side of the mouth.
- Pass the tube between the vocal cords until it reaches the mid-trachea (depth markers can help).
Step 4: Secure the Airway
- Remove the laryngoscope carefully.
- Withdraw the catheter stylet from the tube.
- Attach the resuscitation bag and begin gentle positive pressure ventilation.
🔍 Confirming Proper Intubation
Proper placement is critical. Use the following methods to confirm:
- ✅ Improved heart rate and oxygen saturation
- ✅ Symmetrical breath sounds on both sides of the chest
- ✅ Little or no sound over the stomach (rule out esophageal intubation)
- ✅ Visible chest rise with each breath
- ✅ No stomach distension during ventilation
Simulation Tip: On the Ultrassist Pediatric Intubation Trainer, pink lung balloons inflate if intubation is successful, while the red stomach balloon remains flat. This immediate feedback is ideal for skills assessment and instructor-led evaluation.
Practice Makes Perfect: Why You Need a Neonatal Intubation Trainer
Neonatal intubation requires repeated, guided practice. A high-quality intubation trainer offers:
- Realistic neonatal anatomy for true-to-life intubation
- Compatibility with real clinical tools (ET tubes, laryngoscope, resuscitation bags)
- Tactile feedback for skill refinement
- Support for both oral and nasal intubation
💡 The Ultrassist Neonatal Intubation Trainer is built for repeated use, making it ideal for simulation centers, clinical educators, and emergency training programs.
Neonatal intubation is a life-saving yet high-risk skill. By following a structured, evidence-based approach and integrating simulation-based practice into your training, you can improve your success rate and patient safety.
Train with confidence. Practice with realism.
📦 Get your Ultrassist Neonatal Intubation Trainer today and start building critical neonatal airway skills in a safe, repeatable environment.



.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

