Identifying Critical Neonatal Intubation Landmarks
Successful neonatal intubation relies on precise identification of anatomical landmarks. Mastering these structures helps ensure correct tube placement, prevent airway trauma, and improve clinical outcomes. Below are the essential landmarks every neonatal care provider should know:
1. Vocal Cords:
- Location: At the entrance of the trachea
- Importance: Visualizing the vocal cords confirms that the tube is correctly placed within the trachea. Failure to identify them risks esophageal intubation.
2. Epiglottis:
- Location: Flap-like structure above the glottis
- Importance: Identifying the epiglottis helps guide the laryngoscope blade and avoid misplacement into the esophagus.
3. Cricoid Cartilage:
- Location: Ring-shaped cartilage just below the thyroid cartilage
- Importance: Acts as a landmark for applying cricoid pressure and estimating tube insertion depth.
4. Thyroid Cartilage:
- Location: Front of the neck (more prominent in older children/adults)
- Importance: Serves as an external reference point, especially when the cricoid cartilage is not easily palpable in neonates.
5. Nares (Nostrils):
- Location: Nasal openings
- Importance: Critical entry point during nasal intubation. Proper angle and lubrication are essential for smooth passage.
6. Tragus of the Ear:
- Location: Cartilage in front of the ear canal
- Importance: Aligning the endotracheal tube with the tragus provides a guide for approximate depth during oral intubation.
7. Gum Line:
- Location: Junction between the upper lip and gums
- Importance: Used as a surface reference to gauge how far the tube has been inserted orally.
8. Chest Midline:
- Location: Vertical center of the chest
- Importance: Ensuring tube alignment with the midline helps maintain proper tracheal orientation and avoid bronchial intubation.
9. Xiphoid Process:
- Location: Lower tip of the sternum
- Importance: A reference point to estimate safe tube insertion depth and prevent deep placement into one lung.
10. Endotracheal Tube Markings:
Importance: Always note the centimeter markings on the tube. Secure it based on the recommended insertion depth relative to the baby's weight or gestational age.
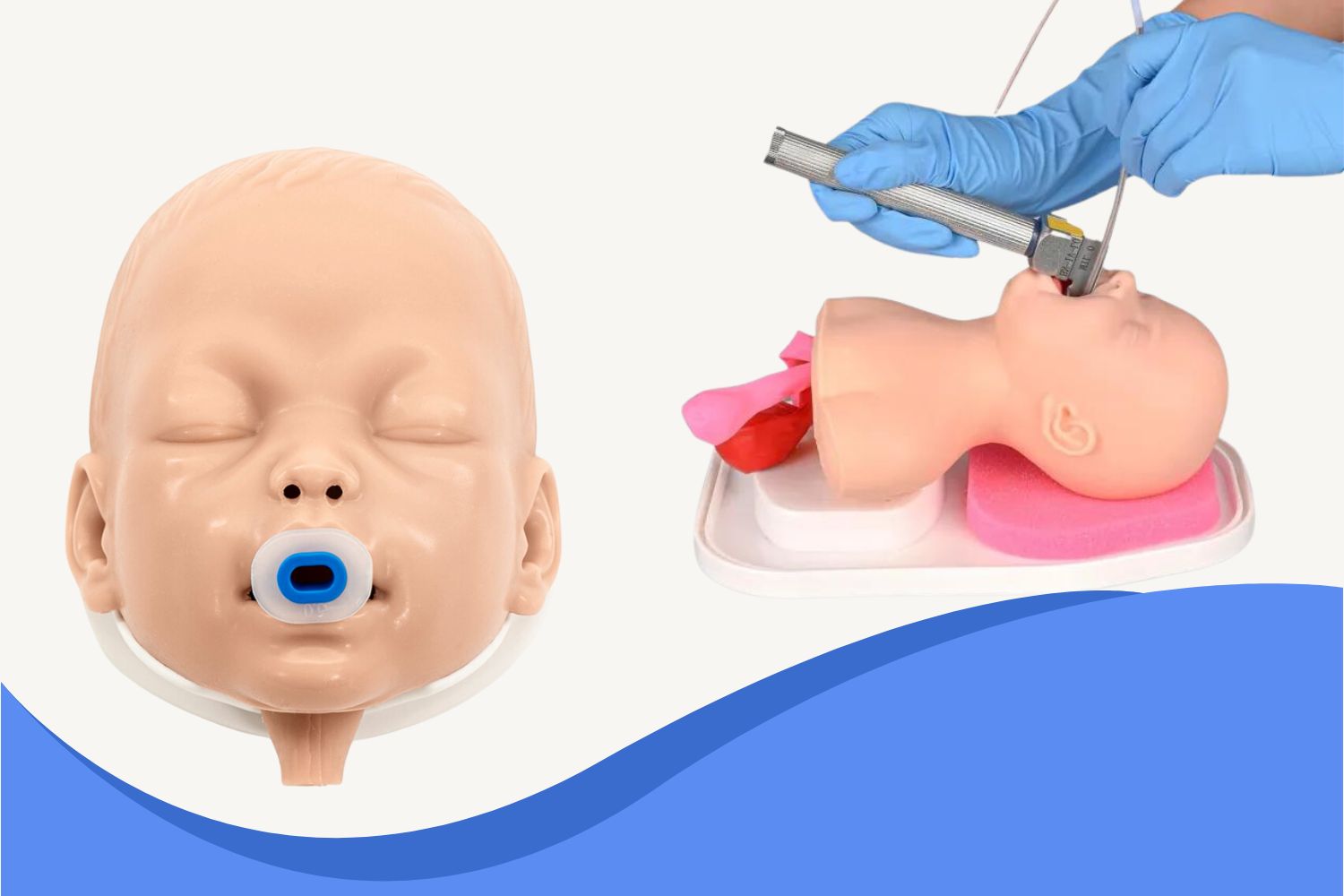
Train With Realism: Practice with Confidence
Visualizing and identifying these landmarks during real procedures can be stressful. That's why hands-on simulation with a high-fidelity manikin is essential. The Ultrassist Pediatric Intubation Trainer offers lifelike anatomy and tactile feedback, making it ideal for mastering intubation techniques.
Pair it with the full Intubation Manikins to build complete respiratory care skills from infants to adults.



.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

.jpeg?w=1500&h=1500)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1600&h=1600)
.jpeg?w=1000&h=1000)

